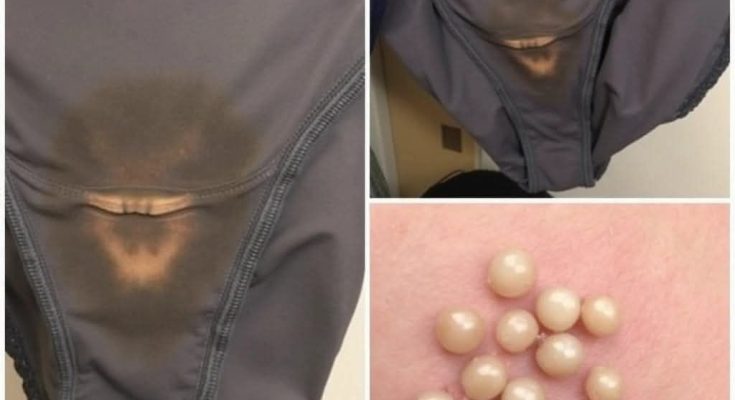
If you spot these dots on your skin, it means you have these Vaginal infections, commonly referred to as vaginitis, occur when the vaginal environment becomes imbalanced, leading to symptoms such as discharge, itching, and discomfort. The condition can be caused by bacterial infections, yeast overgrowth, or other irritants. Hormonal changes, particularly after menopause, can also contribute to an increased risk of vaginal infections.
This article is written under the guidance of medical professionals specializing in reproductive health and women’s wellness.
1. Causes of Vaginal Infections
1.1 Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
Bacterial vaginosis is a common vaginal infection that occurs due to an imbalance in the vaginal microbiome. Normally, lactobacilli dominate the vaginal flora, but when anaerobic bacteria overgrow, they disrupt this balance, leading to BV.
Although BV is often linked to sexual activity, it can also occur in women who are not sexually active due to exposure to bacteria through shared personal items or improper hygiene practices.
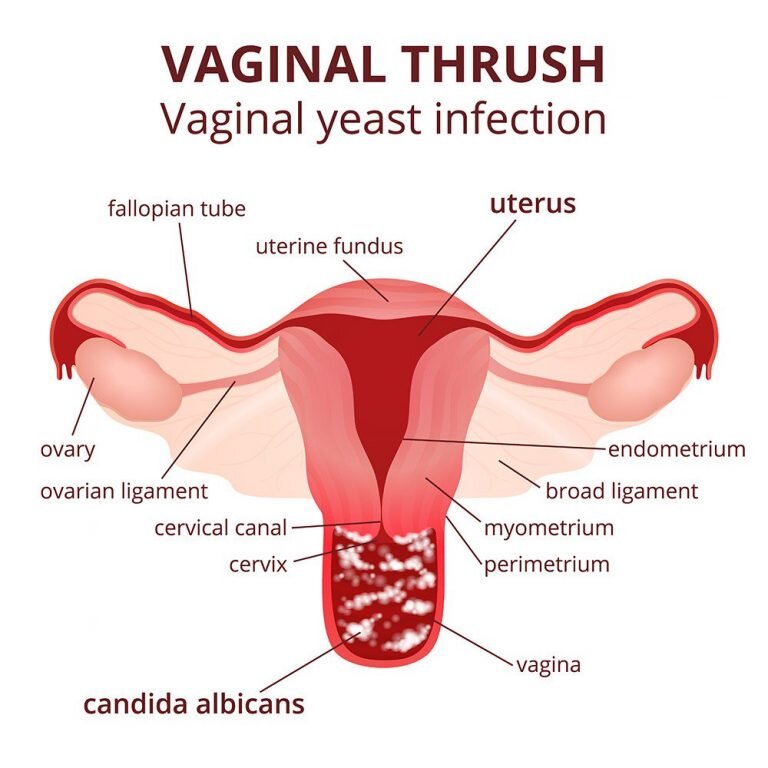
1.2 Yeast Infections
Yeast infections are caused by an overgrowth of Candida albicans, a type of fungus that naturally exists in the body. This overgrowth can occur in moist areas such as the mouth, skin folds, and the vaginal region, leading to discomfort and irritation.
1.3 Trichomoniasis
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the parasite Trichomonas vaginalis. It spreads through sexual contact and primarily affects the vaginal and urinary tract.
Men often carry the parasite without symptoms, while women may experience irritation and discharge. Trichomoniasis also increases susceptibility to other STIs.
1.4 Non-Infectious Vaginitis
Vaginal inflammation can occur due to exposure to irritating substances, such as scented soaps, detergents, or spermicides. Some women may also experience allergic reactions to these products, leading to discomfort and inflammation.
Additionally, foreign objects like forgotten tampons can irritate the vaginal tissues and lead to infections.
1.5 Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause (GSM)
GSM, also known as vaginal atrophy, occurs when estrogen levels decline after menopause or due to surgical removal of the ovaries. This leads to thinning and dryness of the vaginal lining, increasing susceptibility to irritation and infections.
2. Symptoms of Vaginal Infections

If you experience any symptoms of vaginal infection, it is essential to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include:
2.1 Itching and Irritation
Persistent itching in the vaginal area can be an early sign of infection. The severity and duration of itching depend on the underlying cause.
2.2 Abnormal Vaginal Discharge
Healthy vaginal discharge is typically clear or white. Changes in color, consistency, or odor may indicate an infection:
- Thick, white, clumpy discharge suggests a yeast infection.
- Greenish-yellow discharge with a strong odor may indicate trichomoniasis.
- Grayish-white discharge with a fishy odor is a common sign of bacterial vaginosis.
2.3 Pain During Intercourse
Infections can reduce natural lubrication, leading to discomfort and pain during sexual activity.
2.4 Unusual Bleeding
Spotting between periods or post-intercourse bleeding may signal an infection or other underlying health concerns.
2.5 Painful Urination
Burning sensations while urinating can indicate a vaginal infection or a urinary tract infection (UTI), which often coexists with vaginal conditions.
3. Risk Factors for Vaginal Infections
Several factors can increase susceptibility to vaginal infections, including:
- Hormonal changes due to pregnancy, birth control, or menopause.
- Sexual activity, especially with multiple partners.
- Poorly controlled diabetes.
- Use of antibiotics or steroids, which can alter vaginal flora.
- Use of douching products, scented soaps, and synthetic undergarments.
- Prolonged dampness from tight or non-breathable clothing.
4. Treatment of Vaginal Infections

The appropriate treatment depends on the underlying cause of the infection:
4.1 Bacterial Vaginosis
BV is usually treated with oral or topical antibiotics, such as:
- Metronidazole (Flagyl) – available in pill or gel form.
- Clindamycin (Cleocin) – prescribed as a cream applied vaginally.
4.2 Yeast Infections
Over-the-counter antifungal treatments include:
- Miconazole (Monistat)
- Clotrimazole (Gyne-Lotrimin)
- Butoconazole (Femstat)
For recurrent infections, prescription antifungal medications such as fluconazole (Diflucan) may be necessary.
4.3 Trichomoniasis
Antiparasitic medications, including metronidazole or tinidazole, are required to eliminate the infection. Sexual partners should also be treated to prevent reinfection.
4.4 Genitourinary Syndrome of Menopause
Hormone therapy with vaginal estrogen creams, tablets, or rings can help alleviate symptoms. Consult a healthcare provider for personalized treatment options.
4.5 Non-Infectious Vaginitis
Avoiding irritants and identifying potential allergens can help reduce symptoms. Switching to fragrance-free, gentle hygiene products can prevent further irritation.
5. Prevention Strategies

5.1 Proper Hygiene
- Wash the vaginal area with lukewarm water and a mild, unscented cleanser.
- Avoid douching, as it disrupts the natural vaginal flora.
- Wipe from front to back to prevent bacterial transfer from the rectum.
5.2 Menstrual Hygiene
- Change sanitary products every 3-4 hours.
- Wash and dry the area thoroughly before using a new pad or tampon.
5.3 Choosing Breathable Underwear
- Opt for cotton underwear to improve air circulation.
- Avoid tight-fitting clothing that traps moisture and encourages bacterial growth.
5.4 Healthy Diet and Probiotics
- Consume probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt, to support vaginal health.
- Consider probiotic supplements that contain lactobacilli to maintain a balanced vaginal microbiome.
5.5 Regular Gynecological Check-Ups
- Schedule check-ups every six months to detect and address issues early.
- Seek medical advice if you experience unusual symptoms to ensure proper treatment.
Conclusion
Maintaining vaginal health is essential for overall well-being. Practicing good hygiene, choosing appropriate clothing, and following a balanced diet can help prevent infections. If you experience symptoms of a vaginal infection, consult a healthcare professional promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment. Regular medical check-ups also play a crucial role in early detection and prevention of complications.